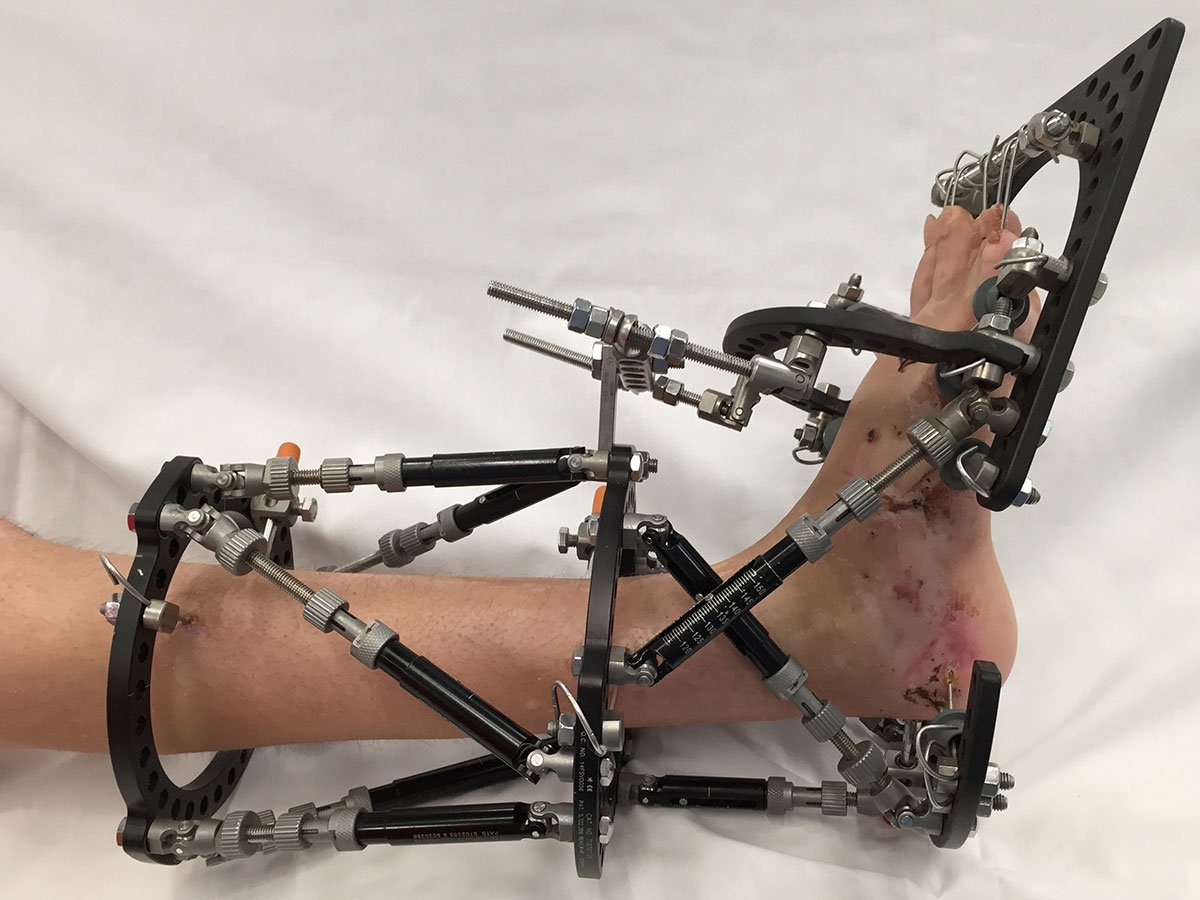
Deformity correction involves the treatment of skeletal abnormalities and misalignments that can result from congenital conditions, trauma, disease, or other causes. These procedures are typically performed by orthopedic surgeons and specialists in musculoskeletal health. The goal is to restore normal function, improve appearance, and alleviate pain. Scoliosis (curvature of the spine), kyphosis (hunchback), and limb length discrepancies. Congenital conditions, trauma, infections, metabolic diseases. Detailed patient history and thorough examination of the affected area. X-rays, CT scans, MRIs to assess the extent and nature of the deformity. Devices to support and align the affected area, often used in children with growing bones. Pain relief and anti-inflammatory drugs to manage symptoms. Surgical cutting and realignment of bones to correct deformities. Use of rods, screws, plates, or nails to stabilize and align bones during healing. Use of external frames and pins to gradually correct deformities over time (e.g., Ilizarov apparatus). Replacing damaged joints with artificial implants, commonly used in severe arthritis. Lengthening or releasing tendons and muscles to correct deformities and improve function. A method of external fixation that gradually corrects bone deformities and length discrepancies.