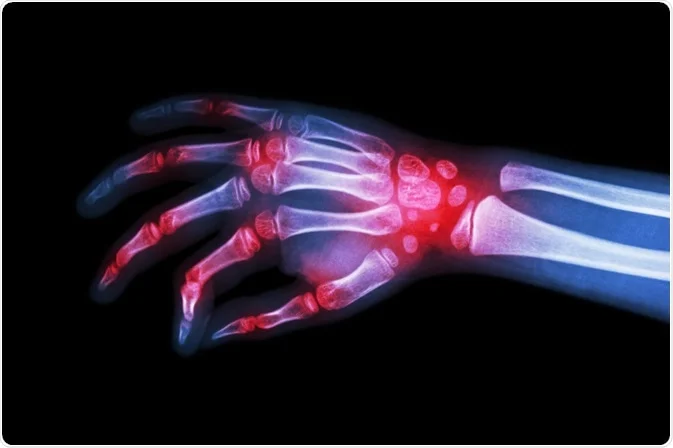
Rheumatology is a branch of medicine that focuses on the diagnosis and treatment of rheumatic diseases, which are characterized by inflammation and pain in the muscles, joints, and connective tissues. Rheumatologists are specialists who manage these conditions, which can be both autoimmune and inflammatory in nature. An autoimmune disorder where the immune system attacks the synovium (lining of the joints). A systemic autoimmune disease affecting multiple organs, including the skin, joints, kidneys, and brain. An inflammatory disease primarily affecting the spine, leading to fusion of the vertebrae. Chronic back pain, stiffness, reduced flexibility, and, in severe cases, a forward-stooped posture. A group of diseases involving hardening and tightening of the skin and connective tissues. Immunosuppressants, corticosteroids, medications for specific symptoms. Thickened skin, Raynaud's phenomenon, digestive issues, organ involvement. Blood tests for inflammatory markers (CRP, ESR), autoantibodies (RF, ANA), and other specific markers.
Rheumatology
Immunology
Immunology is the branch of biomedical science that deals with the study of the immune system, which is responsible for protecting the body against infections, diseases, and foreign substances. The immune system comprises a network of cells, tissues, and organs that work together to defend the body. Immunologists are scientists or clinicians who specialize in this field, focusing on understanding how the immune system functions, malfunctions, and can be manipulated to improve health. The body's second line of defense, which is specific and can remember previous encounters with pathogens. Antibodies (produced by B cells), major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules. Identifying and eliminating harmful microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites. Monitoring the body for abnormal cells, including cancer cells, and initiating an immune response.